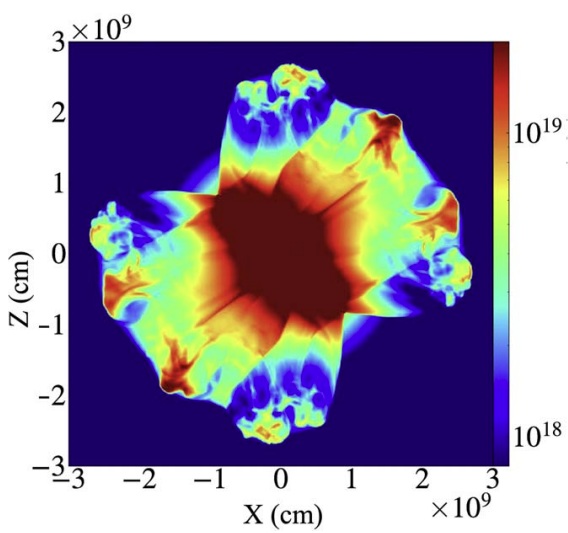
Jessica Braudo (a PhD student) conducted three-dimensional simulations of the jittering-jets explosion mechanism and obtained a point-symmetric explosion, similar to many observed supernova remnants. The paper.
// by Noam Soker

Jessica Braudo (a PhD student) conducted three-dimensional simulations of the jittering-jets explosion mechanism and obtained a point-symmetric explosion, similar to many observed supernova remnants. The paper.
// by Noam Soker
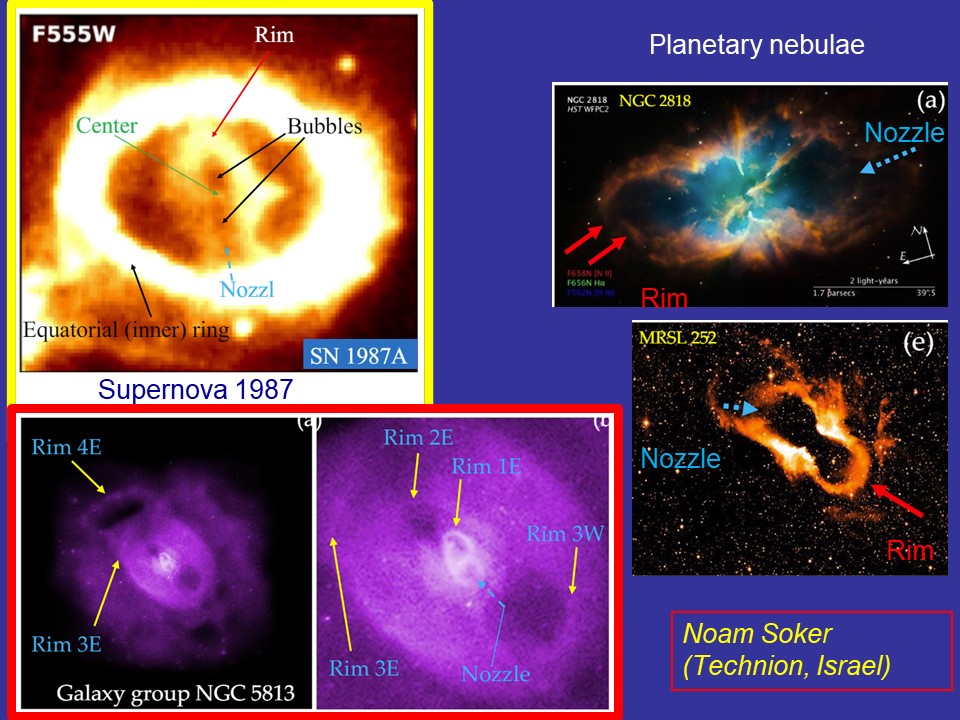 In a series of papers in 2024, I demonstrated the similarities between the morphologies of core-collapse supernovae and other astrophysical objects known to be shaped by jets. This further strengthens the jittering jets explosion mechanism as the primary explosion mechanism of core-collapse supernovae. The competing neutrino-driven explosion mechanism cannot explain these morphologies. I argue that these morphological similarities rule out the neutrino-driven explosion
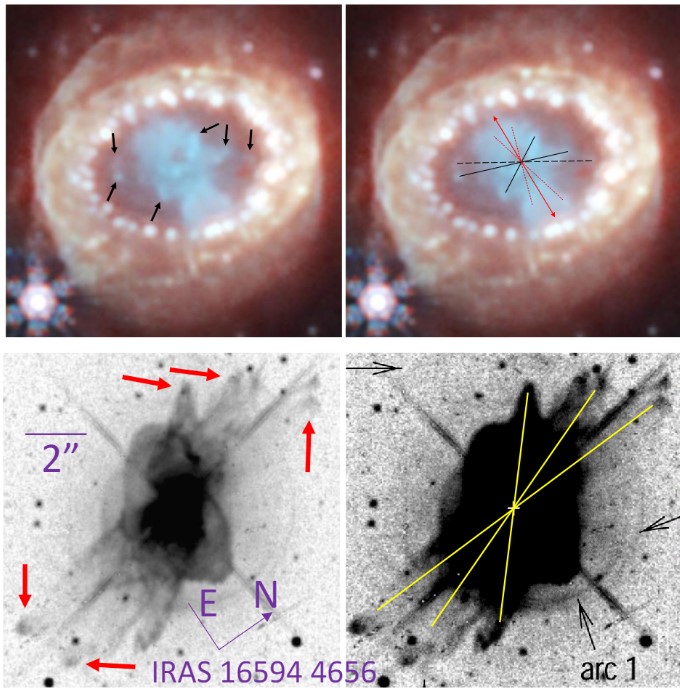
In a series of papers in 2024, I demonstrated the similarities between the morphologies of core-collapse supernovae and other astrophysical objects known to be shaped by jets. This further strengthens the jittering jets explosion mechanism as the primary explosion mechanism of core-collapse supernovae. The competing neutrino-driven explosion mechanism cannot explain these morphologies. I argue that these morphological similarities rule out the neutrino-driven explosion 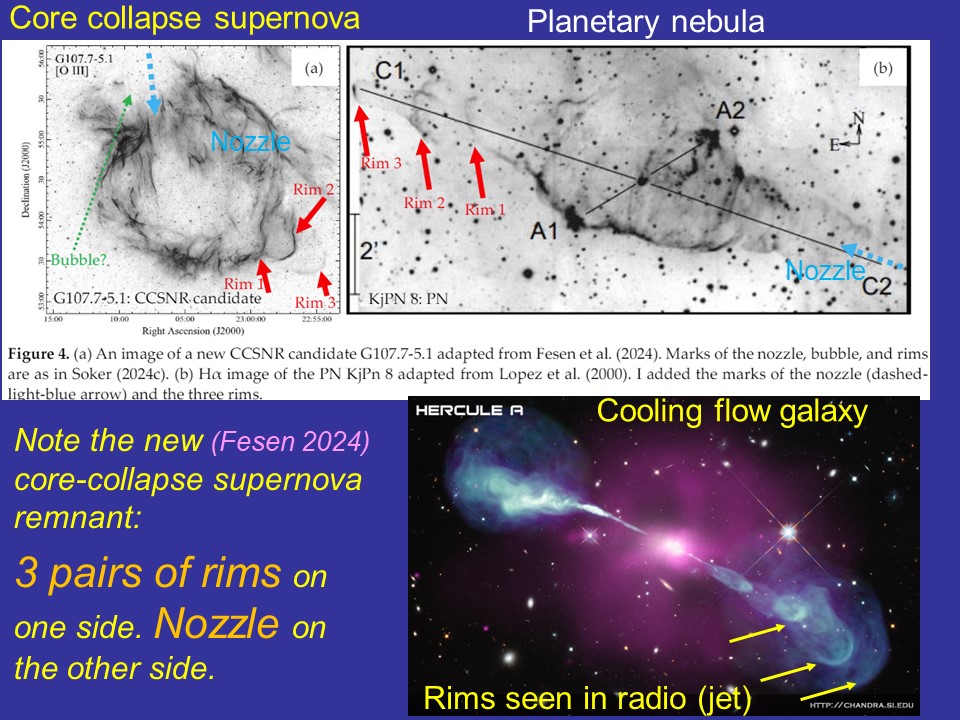 mechanism. Here, I compare the rim-nozzle asymmetry of supernova 1987A to a cluster of galaxies and two planetary nebulae (upper panel), and a newly discovered core-collapse supernova remnant with a cluster of galaxies and with a planetary nebula (lower panel). The paper is here.
mechanism. Here, I compare the rim-nozzle asymmetry of supernova 1987A to a cluster of galaxies and two planetary nebulae (upper panel), and a newly discovered core-collapse supernova remnant with a cluster of galaxies and with a planetary nebula (lower panel). The paper is here.
// by Noam Soker
// by Noam Soker
Shlomi Hillel, Ron Schreier, and I conducted a three-dimensional hydrodynamical simulation of a common envelope evolution where a neutron star spirals-in inside the envelope of a red supergiant star and found that the jets shed pairs of vortices in an expanding spiral pattern (paper).
// by Noam Soker
We (Noam Soker & Ealeal Bear) continue to develop the core degenerate scenario for type Ia supernovae (exploding white dwarfs). We argue that the core degenerate scenario can explain the compact helium-rich circumstellar material of SN 2020eyj. See paper here.
// by Noam Soker
We (Shlomi Hillel, Ron Schreier, Noam Soker) conducted three-dimensional hydrodynamical simulations of common envelope jets supernova (CEJSN) events where we assume that a neutron star (NS) launches jets as it orbits inside the outer zones of a red supergiant (RSG) envelope, and find the negative jet feedback coefficient to be ≃ 0.1 – 0.2. See paper here.
// by Noam Soker
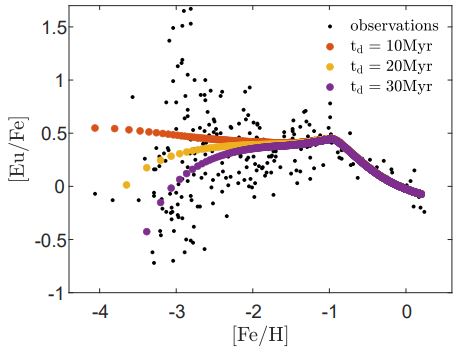
In a paper by Aldana Grichener, Chiaki Kobayashi and Noam Soker we manage to explain the ratio of Europium to iron ratio [Fe/Fe] versus iron to hydrogen ratio [Fe/H] in our galaxy.
// by Noam Soker
In a paper published March 2022 I identify a point-symmetric structure in the velocity maps at the center of the supernova remnant SNR 0540-69.3, and argue that jittering jets that exploded this core collapse supernova shaped this point-symmetric structure.
// by Noam Soker
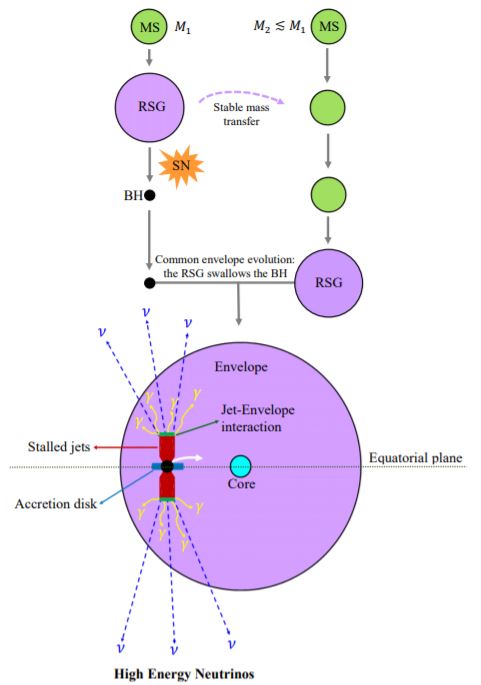
We (Aldana Grichener & Noam Soker) study high energy neutrino emission from relativistic jets launched by a black hole spiraling-in inside the envelope of a red supergiant, and find that such common envelope jets supernovae (CEJSNe) are a potential source for the ~10^15 eV neutrinos detected by IceCube.
// by Noam Soker
I propose a new type of common envelope jets supernova (CEJSN) events where instead of a single neutron star (NS; or a black hole; BH) a tight binary system of a NS and a main sequence star enters a common envelope evolution (CEE) with a red supergiant (for the paper).